Featured products
Ultra Low Quiescent Current Buck-Boost DC/DC Converter for IoT or Wearable Devices
November 12, 2018
RP604 received electronic component award by The Nikken Kogyo Shimbun and MONOZUKURI Nippon Conference.
With the introduction of the RP604 Buck-Boost DC/DC Converter, Nisshinbo Micro Devices has made a large step forward in designing power management ICs with ultra-low current consumption. RP604 is ideally beneficial for use in battery powered devices such as wearables, IoT applications and wireless sensor modules and energy harvesting applications. To reduce valuable PCB space, only three external components are needed. RP604 is available in DFN(PL)2730-12 or ultra-small WLCSP-20-P2.
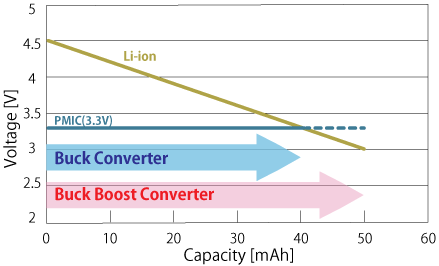
In particular, the RP604 is suitable to use when a supply voltage is required somewhere in between the voltage level of a fully charged and fully discharged battery. At a certain point, the DC/DC converter automatically switches from Buck to Boost mode and vice versa. In this example the Buck-Boost has a significant advantage above a regular Buck DC/DC Converter as it maintains the output voltage setting even if the input voltage drops below the output voltage setting, resulting in a longer operation lifetime of the application.
Li-ion Battery Discharge Curve
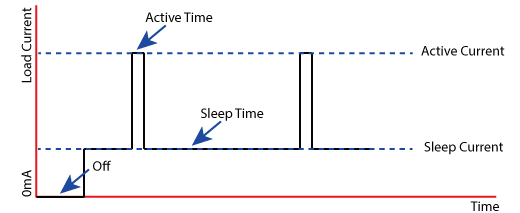
The RP604 is especially designed for applications that are primarily in sleep mode and are periodically activated to take a measurement, send data, and then return to sleep mode. For this type of application, the current consumption in sleep mode must remain as low as possible.
The RP604 has an impressive low quiescent current and uses only 300 nA, which extends the battery life or allows the designer to select a smaller battery for the application.
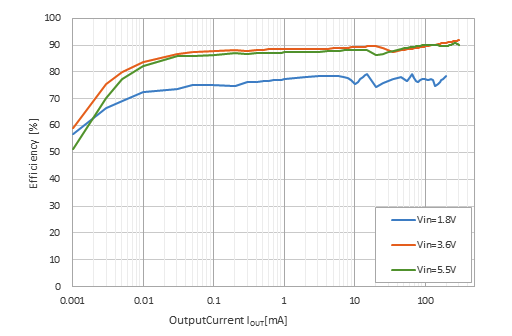
As for the output voltage, it is internally set by laser trimming from 1.6 to 5.2 V in 0.1V step-rate. Peak efficiency is around 92%, depending on input and output conditions. The RP604 has an optional automatic discharge function, which quickly discharges the output capacitor as soon as the chip is disabled by the CE pin.
Output Current vs. Efficiency with Different Input Voltages
RP604Z331x
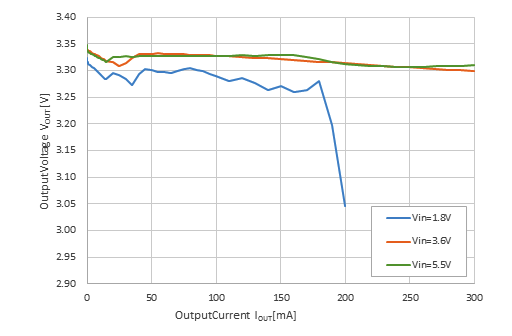
Output Current vs. Output Voltage with Different Input Voltages
RP604Z331x
Protection Circuits:
The RP604 has a number of safety functions that protect the IC and other parts of the application against possible damage and defects, including:
- Under Voltage Lock Out, the DC/DC converter is switched off in case the input voltage falls below a minimum threshold.
- Soft-Start, regulates the output voltage to smoothly rise and prevents any output overshoot and undershoot during the start-up period.
- Lx Current Limit, prevents the peak current through the inductor from exceeding a specific maximum current threshold.
- Output Overvoltage Protection, turns off both the P channel and N channel MOSFETs.
- Thermal Protection, switches the IC off in case the junction temperature rises above 140ºC.
To be used in:
Target applications for this product are small devices, powered from coin batteries, a USB-port or even from an ambient power supply. Such as low-power wireless communication equipment, low-power CPU or MCU, memory, sensor device etc.
Samples and evaluation boards are available through our worldwide regional distributor network as well as online distributors Digi-Key, Mouser and Chip1Stop.
Conclusion
The RP604 Buck-Boost DC/DC converter is a welcome addition to our product range and fits perfectly in portable applications that run on batteries. The very low power consumption is an important key point. The operating voltage ranges from 1.8 to 5.5 V and delivers up to 300 mA in Buck mode, while in Boost mode the output current is less and related to the input voltage level. The output voltage has a seamless transition between buck, buck-boost and boost modes, regardless of whether the input voltage is higher or lower. It is also very suitable for use in energy harvesting applications to optimize the voltage supplied from a capacitor or cell for energy storage.








