When the input voltage was raised steeply from a low value, the output of the DC/DC converter may overshoot. Why did this happen? How should I take measures against this problem?
DC/DC Switching RegulatorsHow to use
The figure below illustrates a typical circuit pattern of a buck DC/DC converter with nonsynchronous rectification (diode rectification).
-
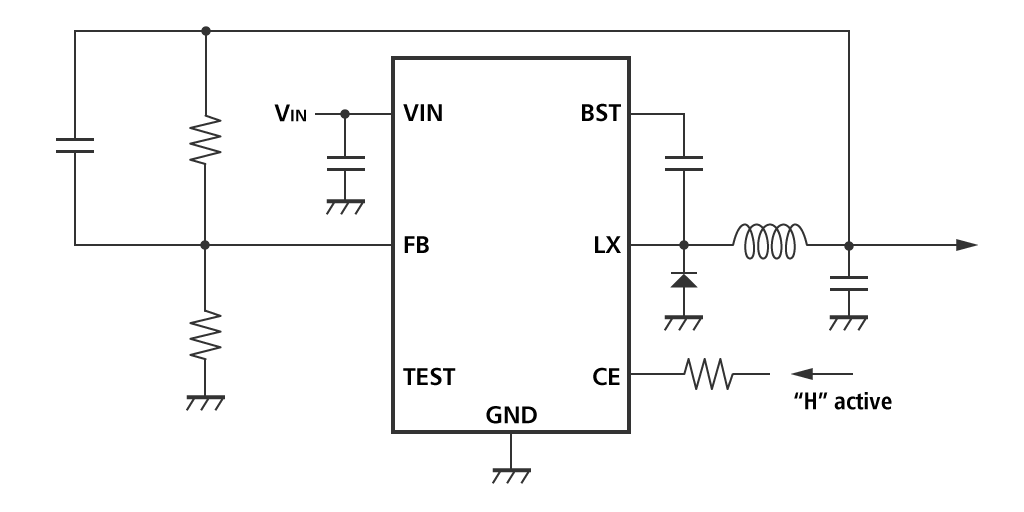
Fig. 1 The typical circuit pattern of a buck DC/DC converter with nonsynchronous rectification
If the potential difference between the input and the output is small and is nearly equal to its maxduty, and if the input voltage is increased steeply from the lower value than the set output voltage, some of buck DC/DC converters may accidentally output as high a voltage as the input voltage, this condition is almost same as input transient response, especially if the VDD and CE tied directly, the threshold of CE pin is relatively low, and soft start time may be expired due to the VIN slow start-up.
To prevent such an overshoot, the following two countermeasures can be effective:
- Increase switching frequency and enhance response speed.
- Make the CE turn 'H' when the input voltage is high enough.
For example, control the CE input by adding a circuit which detects the input voltage has increased sufficiently.
An overshoot will not likely to happen by the soft-start operation when the CE turn from 'L' to 'H'.
The circuit shown as Fig. 2 is an example of the countermeasure. With a zener diode and a resistor, CE pin signal's "L" condition can be extended.
-
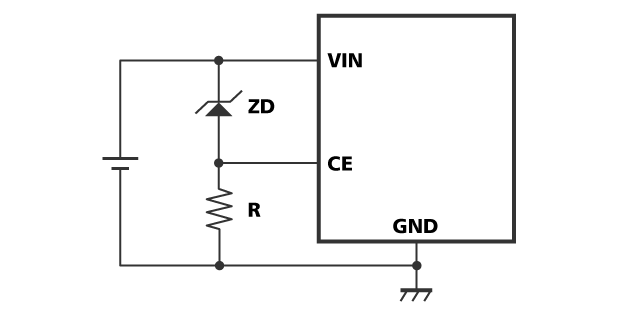
Fig. 2 The circuit with a zener diode and a resistor
Related Products
If you still have questions.
-
Search Other FAQs
-
Enter your question via our web form.







