What is the difference between forced PWM and normal PWM? Which type of PWM control device should I choose in what case?
DC/DC Switching RegulatorsFunction
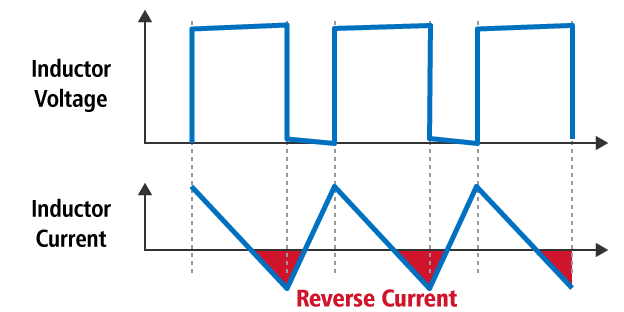
While normal PWM control prevents the reverse current from the inductor at light load, forced PWM control eliminates discontinuous mode by allowing the reverse current from the inductor at light load or even if the input voltage and the output voltage are relatively close.
To avoid the discontinuous mode noise or burst operation, forced PWM type has more advantageous than normal PWM type. Because in the case of forced PWM type, minimum "ON" duty of the switching is fixed by input and output conditions, while normal PWM type is generally continuously going to reduce the "ON" duty of the switching depending on the conditions.
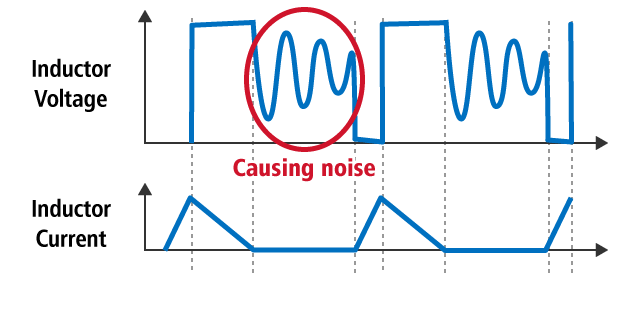
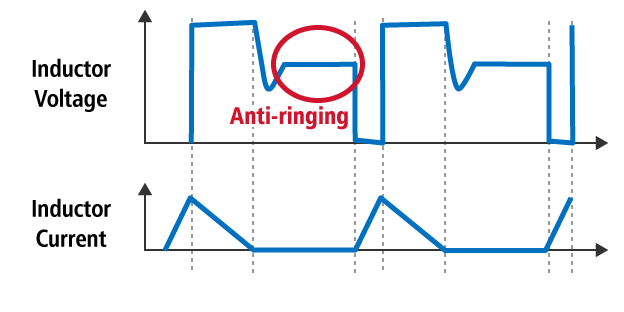
During discontinuous mode, noise can be avoided if the device has the anti-ringing function, but if the voltage difference between input and output is close, the anti-ringing function is not effective.
In most cases, during the discontinuous mode, output voltage ripple is not so large, but at very light load or, if the voltage difference between input and output is close, burst phenomenon may happen and frequency looks slower than the nominal value. In that case, the ripple becomes large. The burst phenomenon is caused by making difficulty of narrow on or off duty switching pulse of the IC. (In fast frequency type, this issue must be cared considering the usage conditions.)
On the other hand, the efficiency at light load of normal PWM is better than forced PWM. Therefore, depending on the priority of output level tolerance, noise, constant frequency or efficiency, choose the appropriate PWM control type. (normal PWM / forced PWM)
-
Normal PWM
-
Normal PWM (Anti-ringing function)
-
Forced PWM
If you still have questions.
-
Search Other FAQs
-
Enter your question via our web form.







