How can I calculate the dropout voltage of an LDO regulator?
LDO Linear RegulatorsHow to use
Dropout voltage (Vdif) refers to the necessary difference between the input and the output voltage to gain fixed output current. Basically, dropout voltage can be calculated at any output current referring to the Dropout Voltage specification written in the datasheet of each product.
Take an example of an LDO regulator whose electrical characteristics are specified in its datasheet as follows: 300 mA, 2.6 V output with dropout voltage of typically 0.23 V.
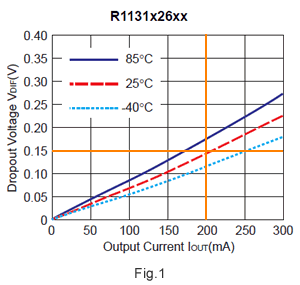
Fig. 1 shows the Dropout Voltage vs. Output Current of the regulator on its datasheet. According to Fig. 1, in order to acquire 200 mA when the temperature is 25°C, the necessary dropout voltage is about 0.15 V. Therefore, the typical minimum input voltage should be about 2.75 V for normal output regulation. You can also figure out the maximum dropout voltage by proportional calculation. The maximum dropout voltage is about 0.23 V, so the minimum input voltage is about 2.83 V.
See datasheets of each product for more details.
Related Products
If you still have questions.
-
Search Other FAQs
-
Enter your question via our web form.







