Electromagnetic Noise: Problems and Perspectives
What Is Noise?
In electronic devices or components, noise is electromagnetic waves which negatively affect their stable operations.
Here are some examples of common noise issues found in our daily life: an audio speaker makes a noise when a nearby microwave appliance is operating; or a clock radio loses time due to the influence of electromagnetic waves from communication devices. The same reason can be applied to why we should refrain from using phones inside a plane or near those using a heart pacemaker because electromagnetic waves from smartphones can have a negative impact on the operation of those precision machines.
To make matters worse, the problem with electromagnetic interference is accelerating and getting harsher as various things around us including cars and home appliances have come to be equipped with communication modules. Special attention should be made to vehicles and cars as they move towards more automation. Strict measures against noise are vital because any malfunction may result in fatal accidents.
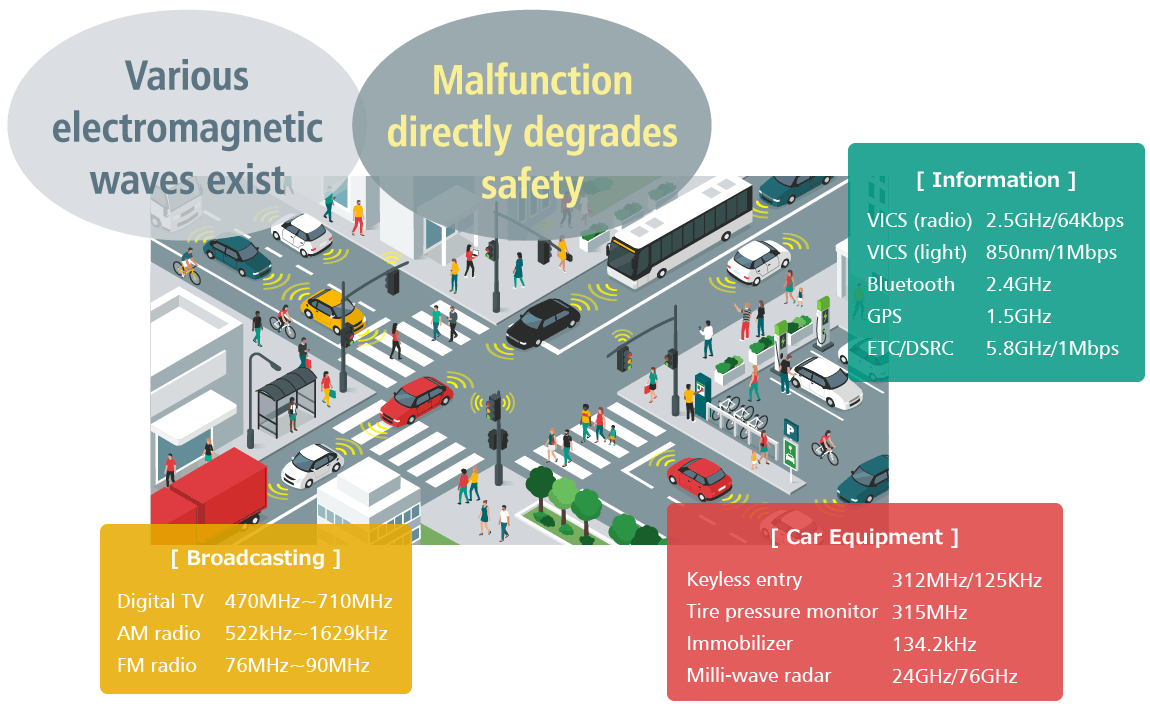
Noise around Automobiles
These days, a wave of rapid change has come in automobiles with "CASE (Connected, Autonomous, Shared & Service, Electric)" and "MaaS (Mobility as a Service)" as megatrends. Furthermore, a shift to electric vehicles (xEVs) is accelerating after 2020 due to global emphasis on carbon neutrality and the number of electronic components used in vehicles is increasing every year. This trend is not only toward electric vehicles and fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). In conventional internal combustion engine vehicles (ICEs), the number of required electronic control units (ECUs) has increased due to the increase in the number of sensors associated with advancements of ADAS and automatic driving, and so has that of electronic components in each of these ECUs significantly.
On the other hand, while radio equipment installed in automobiles used to be mainly for radio and TV broadcast reception systems, the range of applications has expanded with the march of time: from information systems such as navigation systems, to body control systems such as keyless entry systems and tire pressure sensors, and to safety systems such as radars. Accordingly, the frequencies covered have become extremely broad from several hundred kHz to several tens of GHz. Furthermore, due to the increase in the number of electronic devices with communication functions, such as smartphones, conditions of electromagnetic noise in vehicles are becoming more severe than ever before.
Since it is essential that each of the various ECUs installed in automobiles operate under these harsh conditions without giving any electromagnetic influence or without being affected, it is necessary to eliminate potential error factors by preliminary verification. However, the number of failures caused by electromagnetic noise has not been reduced to zero, and accidents may result in loss of life in some cases. Therefore, requirements for safety tests of automobiles and ECUs installed are becoming increasingly strict.
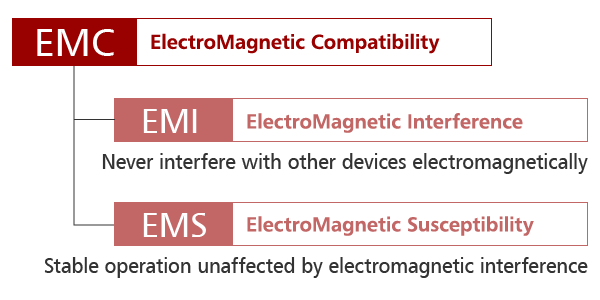
EMC / EMI / EMS Standards
-
-
The importance of countermeasures against electromagnetic noise due to noise from peripheral devices (immunity, EMS) and noise emitted by electronic components (emission, EMI) for semiconductor products mounted on ECUs has been increasing every year.
To achieve social safety and technological evolution, the International Electrotechnical Commission standardized noise countermeasure requirements for electronic devices and components, which are called EMC standards. The word “EMC” stands for Electromagnetic Compatibility.
EMC includes two requirements: Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Electromagnetic Susceptibility (EMS).
In other words, electronic devices and components must meet the requirements both to never generate noise that may affect other devices’ operation and to never be affected by noise from other devices.
After 2020, the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA), a related industry organization, has issued the ED-5008, "EMC performance equivalence test of semiconductor, for the purpose of reducing the burden and cost when replacing components," and the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan (JSAE) has issued the JASO D 019, which describes EMC performance test methods of semiconductors for automotive. The importance of EMC evaluation is increasing not only for vehicles and ECUs but also for semiconductor devices.
Impact of Component Replacement on EMC Measures
Many semiconductor manufacturers have been facing difficulties in continuing to supply the same products for a long time due to relocation and consolidation of production lines for business continuity, as well as change of chips and packages for cost reduction. Therefore, they propose to ECU manufacturers substitute products with equivalent functions and electrical characteristics, or successor products with improved characteristics more frequently.
Although there are cases where component replacement requires no major design changes in terms of basic performance and lets manufacturers continue manufacturing, EMC performance testing (evaluation of noise immunity) may be required again depending on where the components are used. This test takes time and money since it is conducted for a long time using special test facilities such as an anechoic chamber, with the ECU alone or assembled in actual devices. As a result, price for the testing gets higher and time for decision making becomes longer.
In general, these noise immunity evaluations are often conducted at the final stage of vehicle development. If problems are discovered at this stage, design rework from analysis to countermeasures, ECU pattern design, and selection of mounted components may occur. Because of significant impact on design time, switching to alternative semiconductors has become a heavy burden for both semiconductor and equipment manufacturers.
Increasing Importance of Electromagnetic Noise Susceptibility (EMS)
Due to recognized problems associated with immunity (EMS), a list of noise immunity standards was developed along with testing methods and conditions were established for semiconductor components and automotive electronic devices, respectively. To maintain stable operation under an environment full of various electromagnetic noise, high noise immunity is necessary even on the system level.
However, it is often the case that problems occur at immunity testing when there were none before at other characteristic testing. This is due to the difficulty in predicting at what stage of development process noise-related problems happen. Therefore, considering immunity (EMS) countermeasures is one of the main factors that increase development time.
Semiconductor tests
| Test name | International standard |
|---|---|
| General conditions and definitions | IEC 62132-1 |
| TEM cell method | IEC 62132-2 |
| DPI method | IEC 62132-4 |
| WBFC method | IEC 62132-5 |
| IC stripline method | IEC 62132-8 |
To solve the problems mentioned above, we developed power management ICs with high noise immunity against electromagnetic noise using our unique circuit technology.
For those that are troubled or annoyed by immunity testing and EMS countermeasures
-
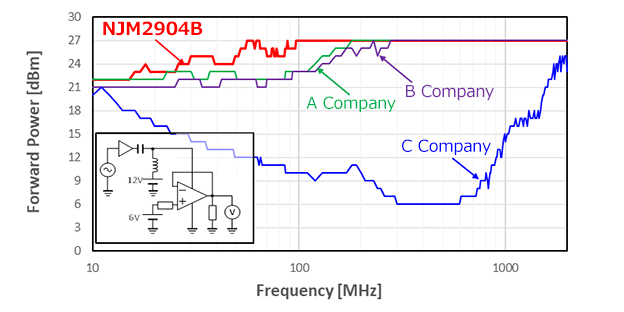
High RF Noise Immunity Operational Amplifiers with Excellent EMC Performance
By minimizing the risk of design rework after the noise evaluation, our operational amplifiers contribute to the reduction of customers' total development costs.
-
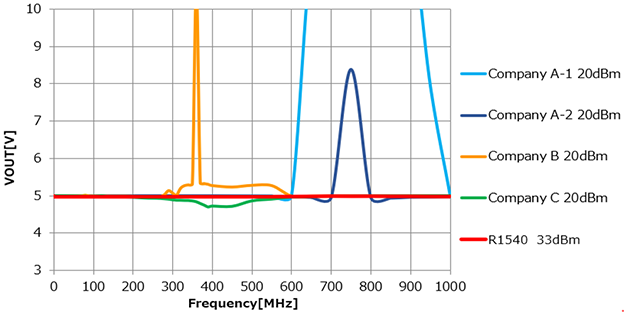
High Noise Immunity Power Management ICs to Combat Against Electromagnetic Noise
We will introduce to you our power management ICs that can supply stable voltage even under noisy environments with wide frequency bands.







